The term "compounding" in the industry actually means "laminating", which is to stick films of different properties together in a certain way and then seal them to protect the contents. The main composite processing methods for flexible packaging include dry composite, wet composite, extrusion composite, co-extrusion composite, etc.
1. Dry laminating
Among various processing technologies of composite films, dry laminating is the most traditional and widely used composite technology in China, and is widely used in the packaging of food, medicine, cosmetics, daily necessities, light industrial products, chemicals, electronic products, etc. Dry laminating is to coat a layer of solvent-based adhesive on the plastic film with a coating device (generally using gravure screen roller coating), remove the solvent and dry it with a laminating machine, and then laminate it with other substrates under hot pressing, such as film, aluminum foil, etc. to form a composite film. The process flow is shown in the figure below. Since it is laminated in the "dry" state of the adhesive (solvent-free state), it is called dry laminating.
Dry laminating is suitable for a variety of composite film substrates and the laminating between film and aluminum foil, paper. It has a wide range of applications and excellent resistance to chemical media erosion. For example, food contains alkali, acid, spicy, oil and other ingredients, cosmetics contain water, flavors, emulsifiers and other ingredients, chemicals contain solvents, pesticides and other ingredients. It is widely used in packaging with harsh content conditions. It has high composite strength, good stability and high product transparency. It can produce high- and medium-grade composite films, as well as frozen, fresh-keeping or high-temperature sterilized composite films; it is convenient and flexible to use, simple to operate, and suitable for the production of multiple varieties and small batches.
However, dry laminating itself also has defects such as poor safety and sanitation, environmental pollution, and high cost. At the same time, the development of alcohol-soluble and water-soluble adhesives has alleviated the pressure of solvent-based adhesives in terms of safety and sanitation, environmental pollution, and cost to a certain extent. Dry laminating still occupies a large proportion in the processing of composite materials, and at this stage it is still a composite processing method that cannot be replaced by extrusion laminating, wet laminating, and solvent-free laminating.
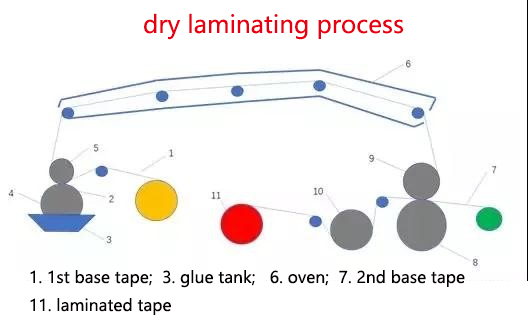
2. Wet Laminating
Wet laminating is to apply a layer of adhesive on the surface of the composite substrate (plastic film, aluminum foil), and then laminating it with other materials (paper, cellophane) through a roller when the adhesive is not dry, and then dry it in a hot drying oven to form a composite film. The characteristics of wet laminating are simple process operation, small amount of adhesive, low cost, and fast laminating speed. The adhesives used in the wet laminating method mainly include polyvinyl alcohol, sodium silicate, starch, polyvinyl acetate, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, polyacrylate, natural resin, etc. The working principle of the wet laminating machine is basically similar to that of the dry laminating. The difference is that the dry laminating is to heat the film coated with adhesive through a drying oven , wait for the organic solvent in the adhesive to volatilize, and then heat-press and bond it with the composite material; while the wet laminating method is to directly laminating the film coated with adhesive with the composite material, and then enter the drying oven for drying.
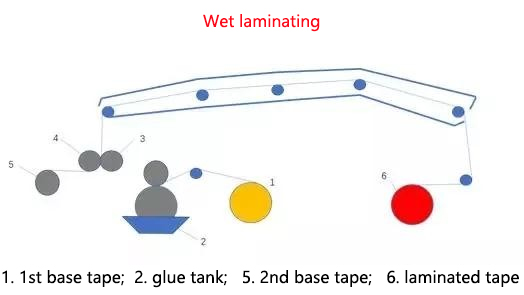
When using wet laminating, at least one of the two substrates is a porous material (such as paper or cardboard) so that the diluent contained in the adhesive can evaporate during drying. Therefore, wet laminating is widely used in the laminating of materials such as paper/fiber, paper/paper, paper/cardboard, and paper/aluminum foil.
3. Extrusion laminating
Extrusion laminating is to melt thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene in an extruder and squeeze them into a flat die. After the sheet-like film flows out, it is immediately laminatinged with another or two films through a cooling roller and a laminating roller. Compared with other laminating methods, extrusion laminating has the advantages of low equipment cost, low investment, clean production environment, no residual solvent in the composite film, high production efficiency, and easy operation. Extrusion laminating occupies a very important position in the composite processing of plastics. Extrusion composite film can be produced by extrusion coating and extrusion laminating.
4. Extrusion coating film
Extrusion coating is a method of melting thermoplastics such as polyethylene and flowing out from a flat die, pressing it against another substrate between two closely contacting rollers, and making a composite film after cooling. The unwinding substrate is generally printed PET, BOPP, paper and other materials. For example, instant noodle packaging bags are a typical example of extrusion coating production, and its structure is: BOPP printed film / LDPE (or PP).
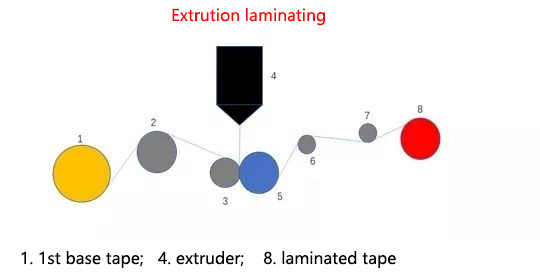
5. Extrusion composite film
Extrusion laminating is to sandwich the extruded resin between two substrates. It acts as an adhesive to combine the two substrates together, and it is also a composite layer. The first substrate is often PET, BOPP, PA, paper and other materials, the second substrate is generally LDPE, CPP, aluminum foil, aluminized film and other materials, and the extruded resin is generally PE, PP, EVA, EAA and other resins. Ordinary washing powder packaging film can be laminatinged by this method, and the structure is as follows: BOPP printed film/extruded resin/PE film.
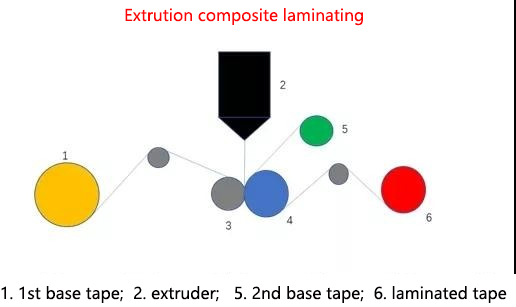
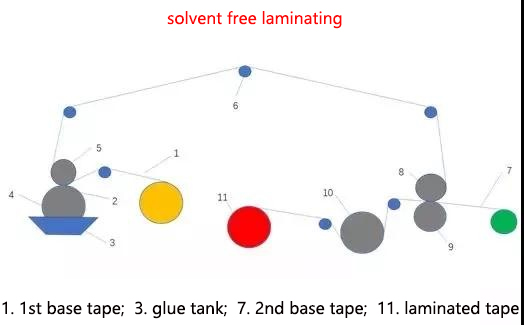
6. Solvent-free laminating
The adhesive used in solvent-free laminating has attracted much attention because it does not contain organic solvents. In developed countries such as Europe and the United States, solvent-free laminating has become the main method for producing composite materials for flexible packaging. It is a laminating method that uses solvent-free adhesive to coat the substrate and directly bonds it to the second substrate. Although it uses adhesives like dry laminating, its adhesive does not contain organic solvents and does not require drying equipment. Due to its superior environmental friendliness, the product performance can also be the same as dry laminating, which is the future development direction.
7. Co-extrusion laminating
a molding method for preparing composite films by melting and plasticizing two or more different plastics through two or more extruders, and then feeding them into a die or combining the plastics supplied by various extruders through a distributor and then feeding them into the die. The different plastics mentioned here can be different types of plastics, or plastics of the same type but different grades, or plastics of the same grade but different formulas.
The cost of co-extrusion laminating is low, which can be reduced by 20%-30% compared with dry laminating. In addition, no adhesive or anchor coating agent (AC agent) is used in the co-extrusion laminating process, so it is hygienic and has no environmental pollution problem. However, due to obvious material limitations, the composite films produced by the co-extrusion laminating process are limited to various thermoplastics. If composite materials containing aluminum foil, paper, etc. are required, they cannot be produced by co-extrusion laminating. In addition, printing cannot be done between composite films. When the film needs to be printed, patterns and texts can only be printed on the surface of the composite film.
Contact: Mr. Carlos
Phone: +86 18638794084
Tel: +86 13673680478
Email: kopymachinery@gmail.com
Add: No.5 Hehuan Street, Gaoxin Dist., 450001, Zhengzhou, China.